Home ::
Consulting
::
Environment, Health & Safety Management
Environment, Health & Safety Management
 »
ISO 14001:2004- Environment Management System
»
ISO 14001:2004- Environment Management System
ISO 14001:2004
An Environment Management System meeting the requirements of ISO 14001:2004 is a management tool enabling an organization of any size or type to:
- identify and control the environmental impact of its activities, products or services, and to
- improve its environmental performance continually, and to
- implement a systematic approach to setting environmental objectives and targets, to achieving these and to demonstrating that they have been achieved.
ISO 14000 series of standards
- ISO 14004:2004 provides guidelines on the elements of an environmental management system and its implementation, and discusses principal issues involved.
- ISO 14001:2004 specifies the requirements for such an environmental management system. Fulfilling these requirements demands objective evidence which can be audited to demonstrate that the environmental management system is operating effectively in conformity to the standard.
Process Approach:
This International Standard promotes the adoption of a process approach when developing, implementing and improving the effectiveness of a quality management system, to enhance customer satisfaction by meeting customer requirements.
In addition, the methodology known as “Plan-Do-Check-Act” (PDCA) can be applied to all processes. PDCA can be briefly described as follows.
Plan: establish the objectives and processes necessary to deliver results in accordance with customer requirements and the organization's policies.
Do: implement the processes.
Check: monitor and measure processes and product against policies, objectives and requirements for the product and report the results.
Act: take actions to continually improve process performance.
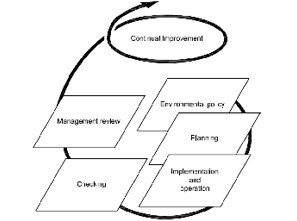
This International Standard specifies requirements for an environmental management system to enable an organization to develop and implement a policy and objectives which take into account legal requirements and information about significant environmental aspects.
There are certain internal and external objectives which can be met by implementing ISO 14001:2004 in your organization. These are
ISO 14001:2004 is a tool that can be used to meet internal objectives:
- provide assurance to management that it is in control of the organizational processes and activities having an impact on the environment
- assure employees that they are working for an environmentally responsible organization.
ISO 14001:2004 can also be used to meet external objectives:
- provide assurance on environmental issues to external stakeholders – such as customers, the community and regulatory agencies
- comply with environmental regulations
- support the organization's claims and communication about its own environmental policies, plans and actions
- provides a framework for demonstrating conformity via suppliers' declarations of conformity, assessment of conformity by an external stakeholder - such as a business client - and for certification of conformity by an independent certification body.
RC 14001 – Responsible care - 14001
The Responsible Care-14001 (RC-14001) environmental management system (EMS), created jointly by the American Chemistry Council (ACC) and the Registrar Accreditation Board (RAB), was formally adopted in 2002.
Responsible Care is the chemical industry’s unique global initiative that drives continuous improvement in health, safety and environmental (HSE) performance, together with open and transparent communication with stakeholders. Responsible Care embraces the development and application of sustainable chemistry, helping our industry contribute to sustainable development while allowing us to meet the world’s growing need for essential chemicals and the products those chemicals make possible
Responsible Care is the chemical industry’s global voluntary initiative under which companies, through their national associations, work to continuously improve their health, safety and environmental performance, and communicate with stakeholders about their products and processes. Responsible Care is the ethical underpinning that enables the creation of essential products that contribute to a sustainable tomorrow. These products and technologies support global efforts to reduce energy use, minimize greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and lighten the human footprint on our earth and its resources. This is Responsible Care.
The chemical industry seeks to live up to the high expectations of its stakeholders by demonstrating that it is a safe and responsible steward of its products, and the processes that create them. Responsible Care companies work with their customers and suppliers to extend their commitments to safety and stewardship throughout the chemistry value chain.
Responsible Care embodies the chemical industry’s commitment to raise its performance around the world. Working with the communities in which they do business, chemical companies are improving their performance while delivering the products that make life better. Responsible Care companies and associations share best practices and support their adoption worldwide. In this spirit, Responsible Care is expanding to emerging chemical economies including Eastern Europe, Russia, China, the Middle East and Africa.
The International Council of Chemical Associations (ICCA) serves as the guardian of Responsible Care globally, monitoring its implementation and ensuring its integrity. Today, 53 chemical industry associations are active in Responsible Care.
OHSAS 18001:2007 – Occupational Health & Safety Management System
OHSAS 18001 was created via the concerted effort from a number of the worlds leading national standards bodies, certification bodies, and specialist consultancies. A main driver for this was to try to remove confusion in the workplace from the proliferation of certifiable OH&S. specifications.
A perhaps would be expected, a number of older documents were used in the creation process. These included:
- BS8800:1996 Guide to occupational health and safety management systems
- Technical Report NPR 5001: 1997 Guide to an occupational health and safety management system
- SGS & ISMOL ISA 2000:1997 Requirements for Safety and Health Management Systems
- BVQI SafetyCert: Occupational Safety and Health Management Standard
- DNV Standard for Certification of Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems(OHSMS):1997
- Draft NSAI SR 320 Recommendation for an Occupational Health and Safety (OH and S) Management System
- Draft AS/NZ 4801 Occupational health and safety management systems Specification with guidance for use
- Draft BSI PAS 088 Occupational health and safety management systems
- UNE 81900 series of pre-standards on the Prevention of occupational risks
- Draft LRQA SMS 8800 Health & safety management systems assessment criteria
It is worth noting that the certification bodies involved in creation hold about 80% of the world market for management system certification.
Why OHSAS?
> Minimize risk to employees and others
> Improve business performance
> Assist organizations in establishing a responsible image within their Marketplace or industry sector
> Ensure an impartial, credible assessment of the OH&S management system
SA 8000 – Social Accountability Management System
SA8000, or "Social Accountability 8000", was developed to promote socially responsible business in all sectors around the globe. Rather than being a "sweatshop code" for customers to enforce upon their suppliers, SA8000 was developed to help socially responsible companies to measure and differentiate themselves from other companies operating with less than acceptable labor conditions. It sets out expectations regarding health and safety, child labor, forced labor, freedom of association, discrimination, disciplinary practices, working hours and compensation together with the management systems to deliver them. SA8000 covers all the major labor rights issues contained in International Labor Organization (ILO) conventions, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child. It also acknowledges the importance of compliance with locally applicable laws.
First published in 1997 and revised in 2001 and 2008, SA8000 has been widely recognized as the most significant tool for bringing workers’ rights business practices into line with the values of society - a vital component of corporate reputation today. The standard is broadly recognized by trade unions, government agencies and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) as one of the strongest workplace standards. Organizations that have recognized SA8000 include the US State Department, the European Commission, the Tuscany Government, the Indian Ministry of Textiles, Business for Social Responsibility and Amnesty International.
SA 8000 Includes
The SA8000 standard and verification system is a credible, comprehensive and efficient tool for assuring humane workplaces because it includes:
- A standard that covers all widely accepted international labor rights.
- Factory-level management system requirement for ongoing compliance and improvement.
- Independent, expert verification of compliance: Certification of facilities by auditing bodies accredited by SAI. SAI accreditation ensures that auditors have the procedures and resources needed to conduct thorough and objective audits. There are currently nine organizations accredited to do SA8000 certification.
- Involvement by all stakeholders: Participation by all key sectors, including workers and trade unions, companies, socially responsible investors, nongovernmental organizations and government, in the SA8000 system. Such participation is required with the Advisory Board, drafting and revision of the standard and auditing system, conferences, training, and the complaints system.
- Harnessing consumer and investor concern: The SA8000 Certification and Corporate Involvement Program help consumers and investors to identify and support companies that are committed to assuring human rights in the workplace SA8000 Standard Elements.
Energy Management System
ISO 50001:2011 - Energy Management System
ISO 50001:2011, Energy management systems – Requirements with guidance for use, is a voluntary International Standard developed by ISO (International Organization for Standardization). ISO 50001 gives organizations the requirements for energy management systems (EnMS).
ISO 50001 will establish a framework for industrial plants; commercial, institutional, and governmental facilities; and entire organizations to manage energy. Targeting broad applicability across national economic sectors, it is estimated that the standard could influence up to 60% of the world’s energy use.
ISO 50001 is based on the management system model that is already understood and implemented by organizations worldwide. It can make a positive difference for organizations of all types in the very near future, while supporting longer term efforts for improved energy technologies.
ISO 50001 is based on the ISO management system model familiar to more than a million organizations worldwide who implement standards such as ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 14001 (environmental management), ISO 22000 (food safety), ISO/IEC 27001 (information security).
In particular, ISO 50001 follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act process for continual improvement of the energy management system.
These characteristics enable organizations to integrate energy management now with their overall efforts to improve quality, environmental management and other challenges addressed by their management systems.
ISO 50001 provides benefits for organizations large and small, in both public and private sectors, in manufacturing and services, in all regions of the world. Like all ISO management system standards, ISO 50001 has been designed for implementation by any organization, whatever its size or activities, whether in public or private sectors, regardless of its geographical location.
ISO 50001 does not fix targets for improving energy performance. This is up to the user organization, or to regulatory authorities. This means than any organization, regardless of its current mastery of energy management, can implement ISO 50001 to establish a baseline and then improve on this at a rhythm appropriate to its context and capacities.